【Spring6】| JdbcTemplate(Spring中的CRUD)
目录
一、JdbcTemplate
1. 环境准备
2. 新增、修改、删除
3. 查询
4. 批量添加、修改、删除
5. 使用回调函数(了解)
6. 使用德鲁伊连接池
一、JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate是Spring提供的一个JDBC模板类,是对JDBC的封装,简化JDBC代码。
当然,你也可以不用!可以让Spring集成其它的ORM框架,例如:MyBatis、Hibernate等。
接下来我们简单来学习一下,使用JdbcTemplate完成增删改查。
1. 环境准备
数据库表准备t_user
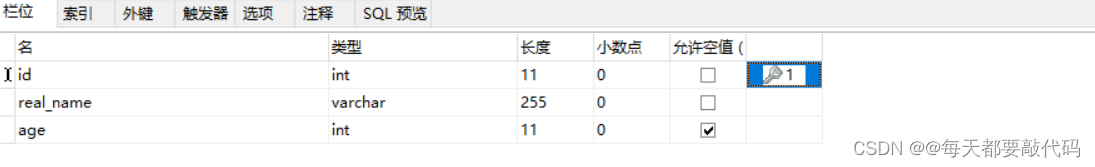
插入数据
新建模块:spring6-008-jdbc
pom.xml中引入相关依赖
4.0.0 com.bjpowernode spring6-008-jdbc 1.0-SNAPSHOT jar repository.spring.milestone Spring Milestone Repository https://repo.spring.io/milestone org.springframework spring-context 6.0.0-M2 junit junit 4.13.2 test mysql mysql-connector-java 8.0.30 org.springframework spring-jdbc 6.0.0-M2 17 17 准备实体类:表t_user对应的实体类User
package com.powernode.spring6.bean;public class User {private Integer id;private String realName;private Integer age;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"id=" + id +", realName='" + realName + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}public User() {}public User(Integer id, String realName, Integer age) {this.id = id;this.realName = realName;this.age = age;}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getRealName() {return realName;}public void setRealName(String realName) {this.realName = realName;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}}
编写数据源DataSource
我们使用JdbcTemplate对象,完成增删改查,所以我们先分析一下源码:
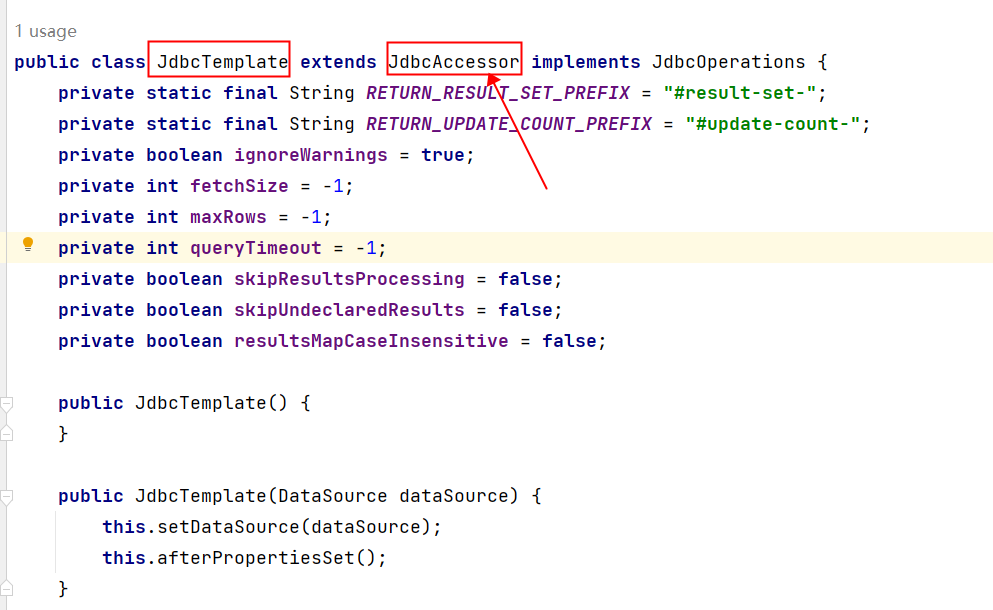
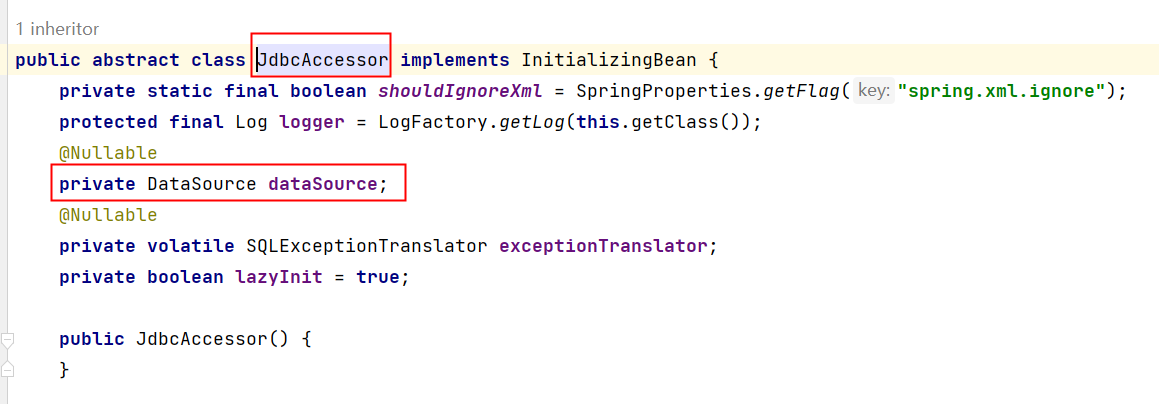
①可以看到JdbcTemplate中有一个DataSource属性,这个属性是数据源,我们都知道连接数据库需要Connection对象,而生成Connection对象是数据源负责的,所以我们需要给JdbcTemplate设置数据源属性。
②所有的数据源都是要实现javax.sql.DataSource接口的。这个数据源可以自己写一个,也可以用写好的,比如:阿里巴巴的德鲁伊连接池druid,c3p0,dbcp等。我们这里自己先手写一个数据源,命名为MyDataSource。
package com.powernode.spring6.jdbc;import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {// 提供连接数据库的属性private String driver;private String url;private String username;private String password;// 提供setter方法public void setDriver(String driver) {this.driver = driver;}public void setUrl(String url) {this.url = url;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}// 重点写怎么获取Connection对象就行,其他方法不用管。@Overridepublic Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {// 获取Connection对象try {// 注册驱动Class.forName(driver);// 获取连接Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);// 返回connection对象return connection;} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return null;}@Overridepublic Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {return 0;}@Overridepublic Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {return null;}@Overridepublic T unwrap(Class iface) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic boolean isWrapperFor(Class iface) throws SQLException {return false;}
}
spring.xml配置
写完数据源MyDataSource,我们需要把这个数据源传递给JdbcTemplate;因为JdbcTemplate中需要一个DataSource属性!
编写测试程序
package com.powernode.spring6.test;import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;public class SpringJdbcTest {@Testpublic void testTest(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);System.out.println(jdbcTemplate);}
}
执行结果:成功创建JdbcTemplate对象
2. 新增、修改、删除
注意:在JdbcTemplate当中,只要是insert、update、delete语句,都是调用update方法。
update方法有两个参数:
①第一个参数:要执行的SQL语句。(SQL语句中可能会有占位符 ? )
②第二个参数:可变长参数,参数的个数可以是0个,也可以是多个;一般是SQL语句中有几个问号,则对应几个参数。
新增
@Testpublic void testInsert(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "insert into t_user(real_name,age) values(?,?)";int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,"王五",20);System.out.println(count);}
修改
@Testpublic void testUpdate(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "update t_user set real_name=?,age=? where id=?";int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,"小红",10,3);System.out.println(count);}
删除
@Testpublic void testDelete(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ?";int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,3);System.out.println(count);}
3. 查询
注意:select语句调用的是queryForObject方法。
queryForObject方法有三个参数:
①第一个参数:sql语句。
②第二个参数:创建一个BeanPropertyRowMapper对象,用来指定属性值和数据库记录行的映射关系,并且调用在构造方法中指定映射的对象类型。
③第三个参数:可变长参数,给sql语句的占位符问号传值。
查询一个对象
调用queryForObject方法,返回的是我们构造方法中指定的对象!
@Testpublic void testSelectOne(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "select id,real_name,age from t_user where id = ?";User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), 1);System.out.println(user);}
查询多个对象
调用的是query方法,返回的是一个List集合,类型是我们构造方法中指定的类型
@Testpublic void testSelectAll() {ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "select id,real_name,age from t_user";List users = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));users.forEach(user -> {System.out.println(user);});} 
查询一个值
调用还是queryForObject方法,返回的肯定是记录的条数,所以指定一下类型是int类型
@Testpublic void testSelectOneValue() {ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "select count(*) from t_user";Integer total = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, int.class);System.out.println("总记录条数是:"+total);}
4. 批量添加、修改、删除
批量增加、修改、删除操作,基本上的步骤都是相同的,都是要先把要操作的数据封装到一个List集合当中;主要的区别就是:执行的SQL不同 和 准备的数据不同!
批量增加
首先把要插入的数据封装到一个List集合当中,然后调用batchUpdate方法,把这个List集合传进去即可
@Testpublic void testBatchInsert(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "insert into t_user(real_name,age) values(?,?)";// 准备要插入的数据Object[] obj1 = {"小花",12};Object[] obj2 = {"小明",14};// 创建List集合List list = new ArrayList<>();// 把数据添加到集合当中list.add(obj1);list.add(obj2);// 执行sql,调用batchUpdate方法int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count)); // [1, 1]} 
批量修改
和批量增加的步骤基本相同!
@Testpublic void testBatchUpdate(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "update t_user set real_name = ?,age = ? where id = ?";// 准备要插入的数据Object[] obj1 = {"小红",18,5};Object[] obj2 = {"小虹",18,6};// 创建List集合List list = new ArrayList<>();// 把数据添加到集合当中list.add(obj1);list.add(obj2);// 执行sql,调用batchUpdate方法int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count)); // [1, 1]} 
批量删除
和批量增加、修改的步骤基本相同!
@Testpublic void testBatchDelete(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ?";// 准备要插入的数据Object[] obj1 = {5};Object[] obj2 = {7};// 创建List集合List list = new ArrayList<>();// 把数据添加到集合当中list.add(obj1);list.add(obj2);// 执行sql,调用batchUpdate方法int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count)); // [1, 1]} 
5. 使用回调函数(了解)
回调函数的作用:如果我们需要编写JDBC代码,就可以使用回调函数;在这个回调函数里就可以编写原生的JDBC代码,步骤如下:
①先调用execute方法,注册回调函数;方法中的参数:第一个参数是sql语句,第二个参数是一个PreparedStatementCallback对象,就是一个回调函数。
②使用回调函数我们要重写里面的doInPreparedStatement方法,这个方法的参数就是原生JDBC中的PreparedStatement对象。
③通过PreparedStatement对象,我们就可以编写下面原生的JDBC代码了
@Testpublic void testCallback(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);// 准备sql语句String sql = "select id,real_name,age from t_user where id = ?";// 注册回调函数// 调用execute方法来注册回调函数:第一个参数是sql语句,第二个参数是一个PreparedStatementCallbackUser user = jdbcTemplate.execute(sql, new PreparedStatementCallback() {@Overridepublic User doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException, DataAccessException {User user = null;// 使用ps进行?赋值ps.setInt(1,2);// 返回一个set集合ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();if (rs.next()){// 获取数据int id = rs.getInt("id");String realName = rs.getString("real_name");int age = rs.getInt("age");// 封装数据user = new User(id,realName,age);}return user;}});System.out.println(user);} 6. 使用德鲁伊连接池
之前的数据源MyDateSource是用我们自己写的;当然也可以使用别人写好的,例如:比较牛的阿里巴巴旗下的德鲁伊连接池(druid)!
第一步:引入德鲁伊连接池的依赖
com.alibaba druid 1.2.13
第二步:将德鲁伊中的数据源配置到spring配置文件中
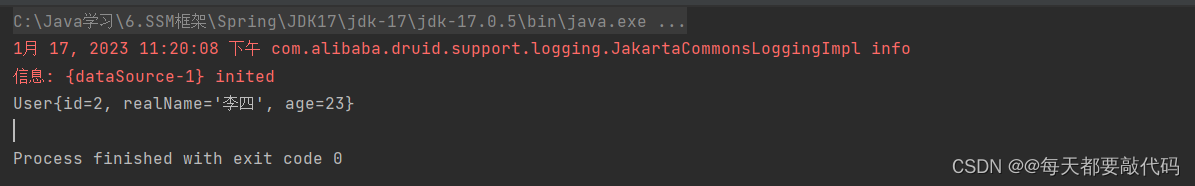
执行结果:
根据输出的信息就能看出使用的确实是德鲁伊连接池