java中的进程和线程的问题
迪丽瓦拉
2025-05-28 12:04:33
0次
进程和线程:
进程是计算机系统资源分配的最小单位,一个进程可以有一个或者多个线程。
线程是计算机运行的最小单位,一个线程只属于一个进程。
一些相关的概念:
单线程:同一个时刻,只允许执行一个线程。
多线程:同一个时刻,可以执行多个线程。
并发和并行: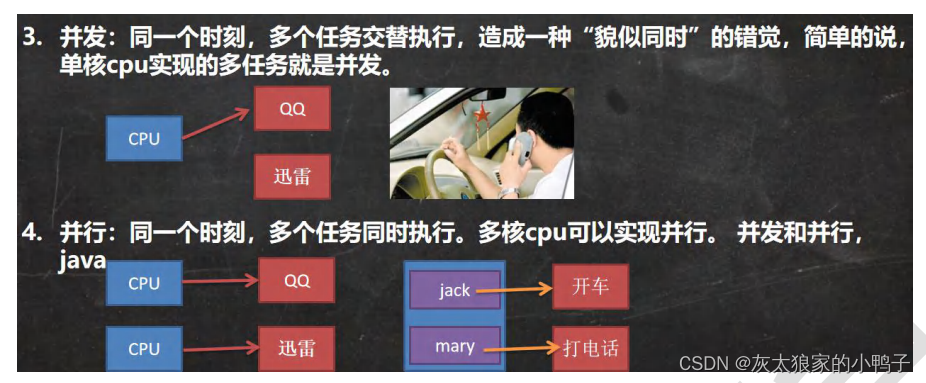
创建线程的方法:
Java 提供了三种创建线程的方法:
- 通过实现 Runnable 接口;
- 通过继承 Thread 类本身;
- 通过 Callable 和 Future 创建线程。
创建线程的例子:
-
使用继承Thread来创建线程:
首先是run()方法里面创建一个进程,然后main方法中开了一个主线程,主线程接着开了一个子线程。主线程与子线程的执行是互不影响的。只有所有的线程都结束了进程才结束。
public class test_thread extends Thread {//主线程:main主线程public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Cat cat = new Cat();cat.start();//主线程中又开启了一个子线程//主线程开启子线程后,不会阻塞:主线程和子线程会交替执行System.out.println("主线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());for (int i=0;i<10;i++){System.out.println("主线程执行 i=" + i);Thread.sleep(1000);}}}//业务需求:
//1. 当Cat类继承了 Thread 类, 该类就可以当做线程使用
//2. 我们会重写 run 方法, 写上自己的业务代码
//3. run Thread 类 实现了 Runnable 接口的 run 方法
class Cat extends Thread{//创建一个线程,Cat类继承了Threadint times=0;//创建了一个进程:@Overridepublic void run() {//重写run方法while (true){System.out.println("喵喵叫。。。。"+(++times) +" "+"子线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());//休眠1stry {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//如果等于8次,退出循环:if (times == 8){break;}}}
}为什么开启子线程需要用start(),而不直接调用run();因为如果直接调用run()方法,此时run()方法就是一个普通的方法。此时的线程就main线程,这时主线程不会开启子线程,只会顺序执行,也就变成了单线程了。
public class test_thread02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Dag dag = new Dag();dag.run();//这时是执行了一个普通的方法,不会开启一个子线程;这时执行的线程是主线程;//此时就变成了单线程了,就是main线程;System.out.println("当前的主线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());for (int i=0;i<9;i++){System.out.println("输出i ="+ i );Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}class Dag extends Thread{//创建一个线程,Cat类继承了Threadint times=0;//创建了一个进程:@Overridepublic void run() {//重写run方法while (true){System.out.println("喵喵叫。。。。"+(++times) +" "+"子线程名:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());//休眠1stry {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//如果等于8次,退出循环:if (times == 8){break;}}}
}喵喵叫。。。。1 子线程名:main
喵喵叫。。。。2 子线程名:main
喵喵叫。。。。3 子线程名:main
喵喵叫。。。。4 子线程名:main
喵喵叫。。。。5 子线程名:main
喵喵叫。。。。6 子线程名:main
喵喵叫。。。。7 子线程名:main
喵喵叫。。。。8 子线程名:main
当前的主线程:main
输出i =0
输出i =1
输出i =2
输出i =3
输出i =4
输出i =5
输出i =6
输出i =7
输出i =8- 实现runnable接口来创建线程:
public class test_runnable {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建子线程:Tiger tiger = new Tiger();//因为runnable接口没有start方法:所以需要动态代理的方式:Thread thread = new Thread(tiger);thread.start();//开启子线程:System.out.println("当前主线程的名字是:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());}
}class Tiger implements Runnable{//实现了Runnable接口:int times=0;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){System.out.println("老虎饿了"+(++times) + " "+"当前的线程名是:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (times == 10){break;}}}
}多线程的使用:
使用实现runnable接口来实现多个线程:
public class test_runnable02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//开启子线程:thread01 thread01 = new thread01();thread02 thread02 = new thread02();Thread td1 = new Thread(thread01);Thread td2 = new Thread(thread02);td1.start();td2.start();}
}class thread01 implements Runnable{//第一个线程int count=0;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){System.out.println("hello thread01" + " "+(++count) +" "+ "当前的进程名字是:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (count == 10){break;}}}
}class thread02 implements Runnable{int count=0;//第二个线程:@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){System.out.println("hello thread02" +" "+(++count)+" "+"当前进程名字是:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (count == 10){break;}}}
}hello thread01 1 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 1 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 2 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 2 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 3 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 3 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 4 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 4 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 5 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 5 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 6 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 6 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 7 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 7 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 8 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 8 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 9 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 9 当前进程名字是:Thread-1
hello thread01 10 当前的进程名字是:Thread-0
hello thread02 10 当前进程名字是:Thread-1继承Thread和实现Runnable接口的区别:
本质上两者没有区别,但是实现Runnable接口更适合多个线程共享资源,并且避免了单继承的机制。
线程常用的方法:
- 第一组:

- 第二组:

相关内容
热门资讯
linux入门---制作进度条
了解缓冲区 我们首先来看看下面的操作: 我们首先创建了一个文件并在这个文件里面添加了...
C++ 机房预约系统(六):学...
8、 学生模块 8.1 学生子菜单、登录和注销 实现步骤: 在Student.cpp的...
A.机器学习入门算法(三):基...
机器学习算法(三):K近邻(k-nearest neigh...
数字温湿度传感器DHT11模块...
模块实例https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38393591/article/deta...
有限元三角形单元的等效节点力
文章目录前言一、重新复习一下有限元三角形单元的理论1、三角形单元的形函数(Nÿ...
Redis 所有支持的数据结构...
Redis 是一种开源的基于键值对存储的 NoSQL 数据库,支持多种数据结构。以下是...
win下pytorch安装—c...
安装目录一、cuda安装1.1、cuda版本选择1.2、下载安装二、cudnn安装三、pytorch...
MySQL基础-多表查询
文章目录MySQL基础-多表查询一、案例及引入1、基础概念2、笛卡尔积的理解二、多表查询的分类1、等...
keil调试专题篇
调试的前提是需要连接调试器比如STLINK。 然后点击菜单或者快捷图标均可进入调试模式。 如果前面...
MATLAB | 全网最详细网...
一篇超超超长,超超超全面网络图绘制教程,本篇基本能讲清楚所有绘制要点&#...
IHome主页 - 让你的浏览...
随着互联网的发展,人们越来越离不开浏览器了。每天上班、学习、娱乐,浏览器...
TCP 协议
一、TCP 协议概念 TCP即传输控制协议(Transmission Control ...
营业执照的经营范围有哪些
营业执照的经营范围有哪些 经营范围是指企业可以从事的生产经营与服务项目,是进行公司注册...
C++ 可变体(variant...
一、可变体(variant) 基础用法 Union的问题: 无法知道当前使用的类型是什...
血压计语音芯片,电子医疗设备声...
语音电子血压计是带有语音提示功能的电子血压计,测量前至测量结果全程语音播报...
MySQL OCP888题解0...
文章目录1、原题1.1、英文原题1.2、答案2、题目解析2.1、题干解析2.2、选项解析3、知识点3...
【2023-Pytorch-检...
(肆十二想说的一些话)Yolo这个系列我们已经更新了大概一年的时间,现在基本的流程也走走通了,包含数...
实战项目:保险行业用户分类
这里写目录标题1、项目介绍1.1 行业背景1.2 数据介绍2、代码实现导入数据探索数据处理列标签名异...
记录--我在前端干工地(thr...
这里给大家分享我在网上总结出来的一些知识,希望对大家有所帮助 前段时间接触了Th...
43 openEuler搭建A...
文章目录43 openEuler搭建Apache服务器-配置文件说明和管理模块43.1 配置文件说明...
