【JavaScript】防抖、节流、深拷贝
认识防抖和节流函数
◾ 防抖和节流的概念其实最早并不是出现在软件工程中,防抖是出现在电子元件中,节流出现在流体流动中
- 而JavaScript是事件驱动的,大量的操作会触发事件,加入到事件队列中处理。
- 而对于某些频繁的事件处理会造成性能的损耗,我们就可以通过防抖和节流来限制事件频繁的发生;
◾ 防抖和节流函数目前已经是前端实际开发中两个非常重要的函数,也是面试经常被问到的面试题。
◾但是很多前端开发者面对这两个功能,有点摸不着头脑:
- 某些开发者根本无法区分防抖和节流有什么区别(面试经常会被问到);
- 某些开发者可以区分,但是不知道如何应用;
- 某些开发者会通过一些第三方库来使用,但是不知道内部原理,更不会编写;
◾接下来我们会一起来学习防抖和节流函数:
- 我们不仅仅要区分清楚防抖和节流两者的区别,也要明白在实际工作中哪些场景会用到;
- 并且我会带着大家一点点来编写一个自己的防抖和节流的函数,不仅理解原理,也学会自己来编写;
认识防抖debounce函数
🟩 我们用一副图来理解一下它的过程:
🟢 当事件触发时,相应的函数并不会立即触发,而是会等待一定的时间;
🟢 当事件密集触发时,函数的触发会被频繁的推迟;
🟢 只有等待了一段时间也没有事件触发,才会真正的执行响应函数; 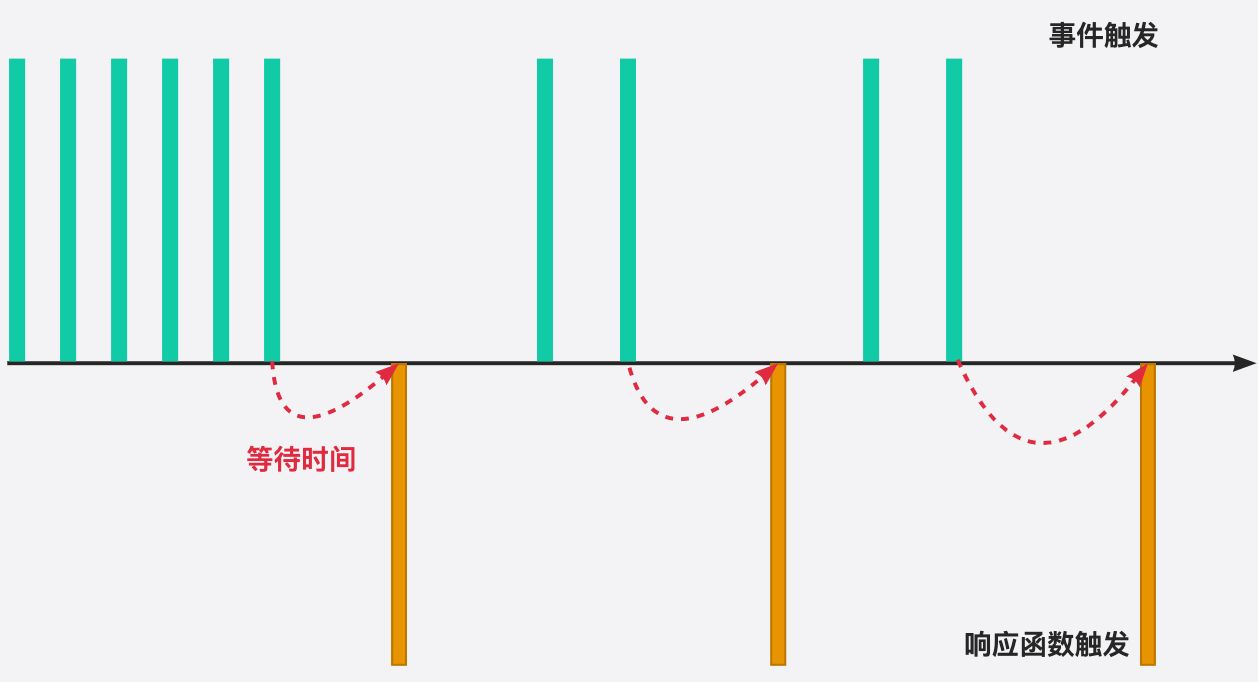
💠 防抖的应用场景很多:
➢ 输入框中频繁的输入内容,搜索或者提交信息;
➢ 频繁的点击按钮,触发某个事件;
➢ 监听浏览器滚动事件,完成某些特定操作;
➢ 用户缩放浏览器的resize事件;
防抖函数的案例
我们都遇到过这样的场景,在某个搜索框中输入自己想要搜索的内容:
💠 比如想要搜索一个MacBook:
- 当我输入m时,为了更好的用户体验,通常会出现对应的联想内容,这些联想内容通常是保存在服务器的,所以需要一次网络请求;
- 当继续输入ma时,再次发送网络请求;
- 那么macbook一共需要发送7次网络请求;
- 这大大损耗我们整个系统的性能,无论是前端的事件处理,还是对于服务器的压力;
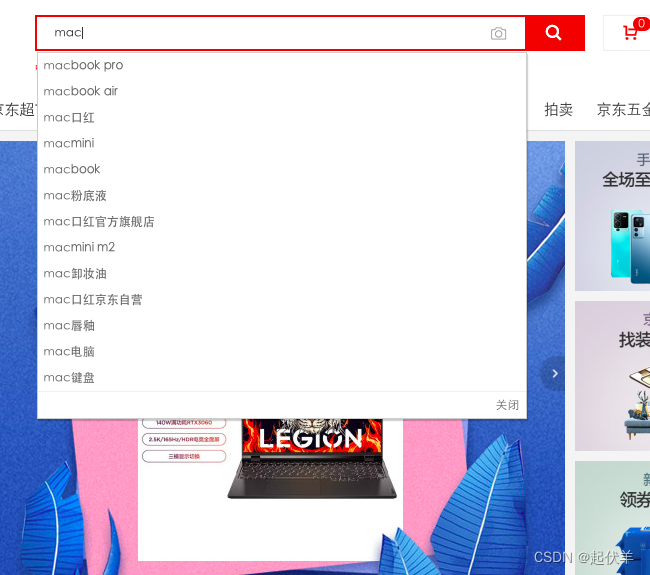
❓ 但是我们需要这么多次的网络请求吗?
✅ 不需要,正确的做法应该是在合适的情况下再发送网络请求;
- 比如如果用户快速的输入一个macbook,那么只是发送一次网络请求;
- 比如如果用户是输入一个m想了一会儿,这个时候m确实应该发送一次网络请求;
- 也就是我们应该监听用户在某个时间,比如500ms内,没有再次触发时间时,再发送网络请求;
这就是防抖的操作:_只有在某个时间内,没有再次触发某个函数时,才真正的调用这个函数;
认识节流throttle函数
🟩 我们用一副图来理解一下节流的过程:
🟢 当事件触发时,会执行这个事件的响应函数;
🟢 如果这个事件会被频繁触发,那么节流函数会按照一定的频率来执行函数;
🟢 不管在这个中间有多少次触发这个事件,执行函数的频繁总是固定的;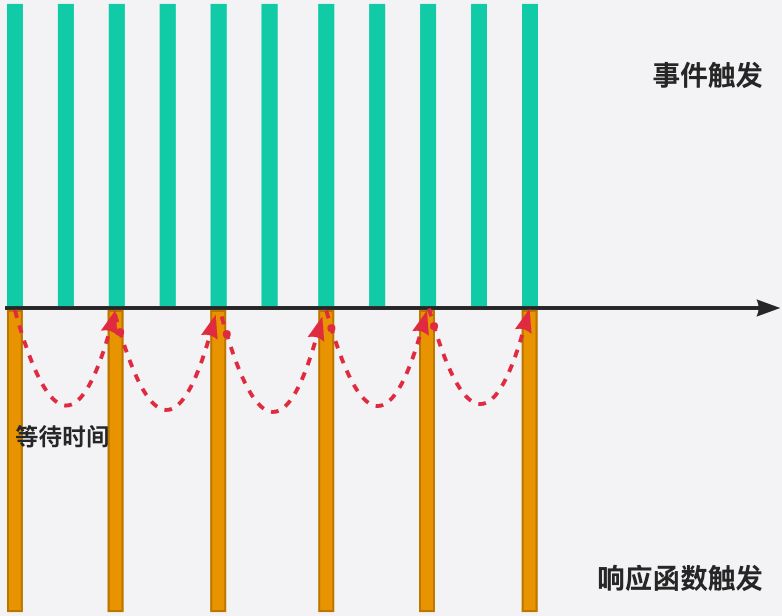
💠 节流的应用场景:
➢ 监听页面的滚动事件;
➢ 鼠标移动事件;
➢ 用户频繁点击按钮操作;
➢ 游戏中的一些设计;
节流函数的应用场景
◼ 很多人都玩过类似于飞机大战的游戏
◼ 在飞机大战的游戏中,我们按下空格会发射一个子弹:
- 很多飞机大战的游戏中会有这样的设定,即使按下的频率非常快,子弹也会保持一定的频率来发射;
- 比如1秒钟只能发射一次,即使用户在这1秒钟按下了10次,子弹会保持发射一颗的频率来发射;
- 但是事件是触发了10次的,响应的函数只触发了一次;
生活中的例子:防抖和节流
◼ 生活中防抖的例子:
◼ 比如说有一天我上完课,我说大家有什么问题来问我,我会等待五分钟的时间。
◼ 如果在五分钟的时间内,没有同学问我问题,那么我就下课了;
- 在此期间,a同学过来问问题,并且帮他解答,解答完后,我会再次等待五分钟的时间看有没有其他同学问问题;
- 如果我等待超过了5分钟,就点击了下课(才真正执行这个时间);
◼ 生活中节流的例子:
◼ 比如说有一天我上完课,我说大家有什么问题来问我,但是在一个5分钟之内,不管有多少同学来问问题,我只会解答一个问题;
◼ 如果在解答完一个问题后,5分钟之后还没有同学问问题,那么就下课;
Underscore库的介绍
◼ 事实上我们可以通过一些第三方库来实现防抖操作:
lodash
underscore
◼ 这里使用underscore我们可以理解成lodash是underscore的升级版,它更重量级,功能也更多;但是目前我看到underscore还在维护,lodash已经很久没有更新了;
◼ Underscore的官网: https://underscorejs.org/
◼ Underscore的安装有很多种方式: 下载Underscore,本地引入;通过CDN直接引入;通过包管理工具(npm)管理安装;
◼ 这里我们直接通过CDN:
自定义防抖和节流函数
防抖
我们按照如下思路来实现:
防抖基本功能实现:可以实现防抖效果
function hydebounce(fn, delay) {// 1.用于记录上一次事件触发的timerlet timer = null// 2.触发事件时执行的函数const _debounce = () => {// 2.1.如果有再次触发(更多次触发)事件, 那么取消上一次的事件if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)// 2.2.延迟去执行对应的fn函数(传入的回调函数)timer = setTimeout(() => {fn()timer = null // 执行过函数之后, 将timer重新置null}, delay);}// 返回一个新的函数return _debounce
}// 1.获取input元素
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
// 3.自己实现的防抖
let counter = 1
inputEl.oninput = hydebounce(function() {console.log(`发送网络请求${counter++}`)
}, 1000)
优化一:优化参数和this指向
function hydebounce(fn, delay) {// 1.用于记录上一次事件触发的timerlet timer = null// 2.触发事件时执行的函数const _debounce = function(...args) {// 2.1.如果有再次触发(更多次触发)事件, 那么取消上一次的事件if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)// 2.2.延迟去执行对应的fn函数(传入的回调函数)timer = setTimeout(() => {fn.apply(this, args)timer = null // 执行过函数之后, 将timer重新置null}, delay);}// 返回一个新的函数return _debounce
}let counter = 1
inputEl.oninput = hydebounce(function(event) {console.log(`发送网络请求${counter++}:`, this, event)
}, 1000)
优化二:优化取消操作(增加取消功能)
function hydebounce(fn, delay) {// 1.用于记录上一次事件触发的timerlet timer = null// 2.触发事件时执行的函数const _debounce = function(...args) {// 2.1.如果有再次触发(更多次触发)事件, 那么取消上一次的事件if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)// 2.2.延迟去执行对应的fn函数(传入的回调函数)timer = setTimeout(() => {fn.apply(this, args)timer = null // 执行过函数之后, 将timer重新置null}, delay);}// 3.给_debounce绑定一个取消的函数_debounce.cancel = function() {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)}// 返回一个新的函数return _debounce
}// --------
let counter = 1
const debounceFn = hydebounce(function(event) {console.log(`发送网络请求${counter++}:`, this, event)
}, 5000)
inputEl.oninput = debounceFn// 4.实现取消的功能
cancelBtn.onclick = function() {debounceFn.cancel()
}
优化三:优化立即执行效果(第一次立即执行)
function hydebounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {// 1.用于记录上一次事件触发的timerlet timer = nulllet isInvoke = false// 2.触发事件时执行的函数const _debounce = function(...args) {// 2.1.如果有再次触发(更多次触发)事件, 那么取消上一次的事件if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)// 第一次操作是不需要延迟if (immediate && !isInvoke) {fn.apply(this, args)isInvoke = truereturn}// 2.2.延迟去执行对应的fn函数(传入的回调函数)timer = setTimeout(() => {fn.apply(this, args)timer = null // 执行过函数之后, 将timer重新置nullisInvoke = false}, delay);}// 3.给_debounce绑定一个取消的函数_debounce.cancel = function() {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)timer = nullisInvoke = false}// 返回一个新的函数return _debounce
}let counter = 1
const debounceFn = hydebounce(function(event) {console.log(`发送网络请求${counter++}:`, this, event)
}, 100)
inputEl.oninput = debounceFn// 4.实现取消的功能
cancelBtn.onclick = function() {debounceFn.cancel()
}
优化四:优化返回值
// 原则: 一个函数进行做一件事情, 一个变量也用于记录一种状态function hydebounce(fn, delay, immediate = false, resultCallback) {// 1.用于记录上一次事件触发的timerlet timer = nulllet isInvoke = false// 2.触发事件时执行的函数const _debounce = function(...args) {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {try {// 2.1.如果有再次触发(更多次触发)事件, 那么取消上一次的事件if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)// 第一次操作是不需要延迟let res = undefinedif (immediate && !isInvoke) {res = fn.apply(this, args)if (resultCallback) resultCallback(res)resolve(res)isInvoke = truereturn}// 2.2.延迟去执行对应的fn函数(传入的回调函数)timer = setTimeout(() => {res = fn.apply(this, args)if (resultCallback) resultCallback(res)resolve(res)timer = null // 执行过函数之后, 将timer重新置nullisInvoke = false}, delay);} catch (error) {reject(error)}})}// 3.给_debounce绑定一个取消的函数_debounce.cancel = function() {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)timer = nullisInvoke = false}// 返回一个新的函数return _debounce
}// 1.获取input元素
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector(".cancel")// 2.手动绑定函数和执行
const myDebounceFn = hydebounce(function(name, age, height) {console.log("----------", name, age, height)return "coderwhy 哈哈哈哈"
}, 1000, false)myDebounceFn("why", 18, 1.88).then(res => {console.log("拿到执行结果:", res)
})
节流
我们按照如下思路来实现:
节流函数的基本实现:可以实现节流效果
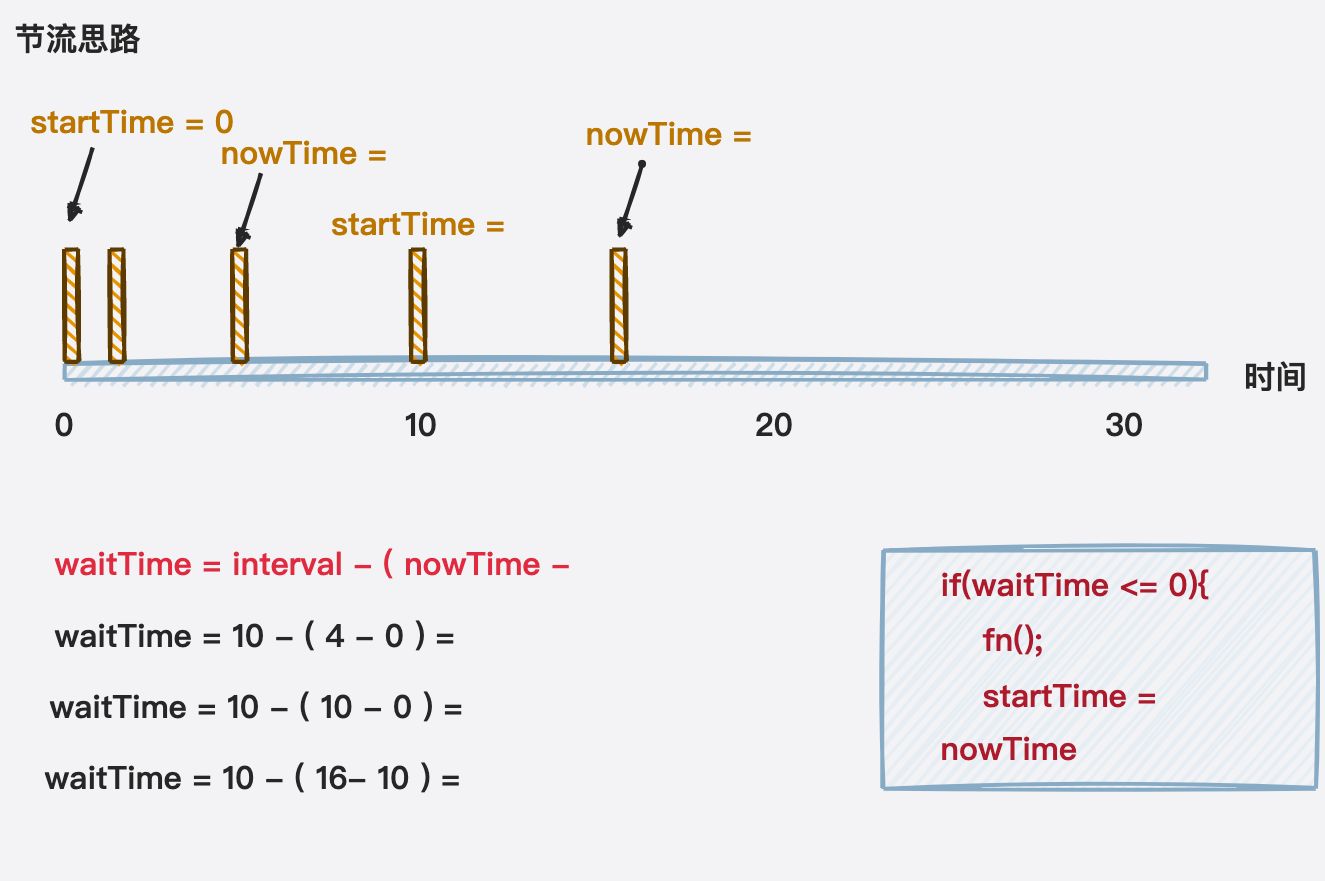
function mythrottle(fn, interval) {let startTime = 0;const _throttle = function (...args) {const nowTime = new Date().getTime();const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime);if (waitTime <= 0) {fn.apply(this, args);startTime = nowTime;}}return _throttle
}
const inputCxt = document.querySelector("input");
const btnSend = document.querySelector("button");
let count = 1;inputCxt.oninput = mythrottle(function (event) {console.log(`第${count++}发出请求:`, this.value, event)
}, 3000);优化一:节流最后一次也可以执行
节流函数默认立即执行
function mythrottle(fn, interval, leading = true) {let startTime = 0;const _throttle = function (...args) {const nowTime = new Date().getTime();// 控制立即执行if (!leading && startTime === 0) {startTime = nowTime}const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime);if (waitTime <= 0) {fn.apply(this, args);startTime = nowTime;}}return _throttle
}
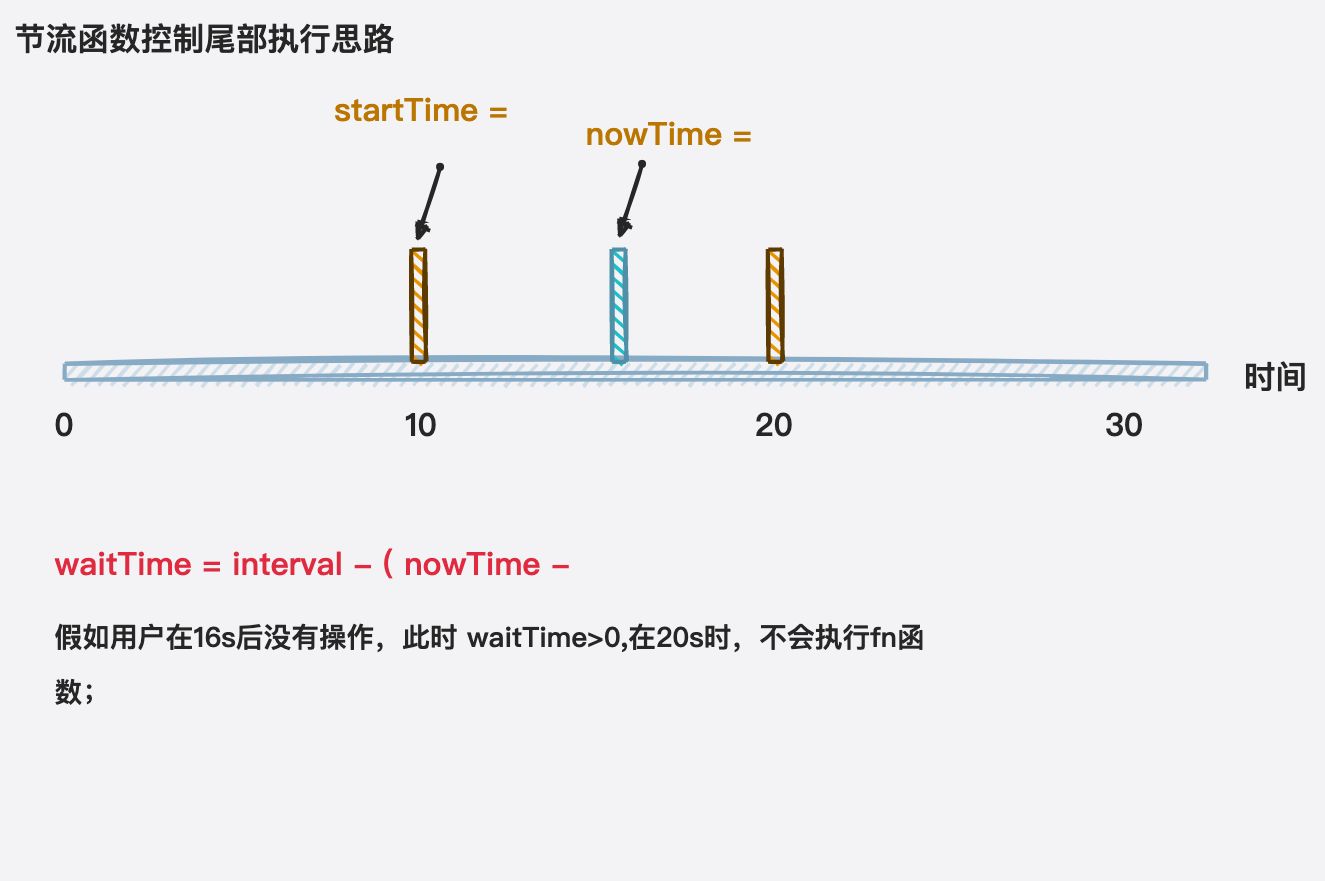
function mythrottle(fn, interval, { leading = true, trailing = false } = {}) {let startTime = 0;let timer = null;const _throttle = function (...args) {const nowTime = new Date().getTime();// 控制立即执行if (!leading && startTime === 0) {startTime = nowTime}const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime);if (waitTime <= 0) {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);fn.apply(this, args);startTime = nowTime;timer = null;return}// 判断是否要执行尾部if (trailing && !timer) {// 尾部的执行时间timer = setTimeout(() => {fn.apply(this, args);startTime = new Date().getTime();timer = null;}, waitTime);}}return _throttle
}
优化二:优化添加取消功能
function mythrottle(fn, interval, { leading = true, trailing = false } = {}) {let startTime = 0;let timer = null;const _throttle = function (...args) {const nowTime = new Date().getTime();// 控制立即执行if (!leading && startTime === 0) {startTime = nowTime}const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime);if (waitTime <= 0) {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);fn.apply(this, args);startTime = nowTime;timer = null;return}// 判断是否要执行尾部if (trailing && !timer) {// 尾部的执行时间timer = setTimeout(() => {fn.apply(this, args);startTime = new Date().getTime();timer = null;}, waitTime);}}// 取消_throttle.cancel = function () {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);startTime = 0;timer = null;}return _throttle
}
const inputCxt = document.querySelector("input");
const btnSend = document.querySelector("button");
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector(".cancel");
let count = 1;const throttle = mythrottle(function (event) {console.log(`第${count++}发出请求:`, this.value, event)
}, 1000, { trailing: true });inputCxt.oninput = throttle;
cancelBtn.onclick = function () {throttle.cancel();
}
优化三:优化返回值问题
function mythrottle(fn, interval, { leading = true, trailing = false } = {}) {let startTime = 0;let timer = null;const _throttle = function (...args) {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {try {const nowTime = new Date().getTime();// 控制立即执行if (!leading && startTime === 0) {startTime = nowTime}const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime);if (waitTime <= 0) {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);const res = fn.apply(this, args);resolve(res);startTime = nowTime;timer = null;return}// 判断是否要执行尾部if (trailing && !timer) {// 尾部的执行时间timer = setTimeout(() => {const res = fn.apply(this, args);resolve(res);startTime = new Date().getTime();timer = null;}, waitTime);}} catch (error) {reject(error)}})}// 取消_throttle.cancel = function () {if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);startTime = 0;timer = null;}return _throttle
}
const throttle = mythrottle(function (event) {console.log(`第${count++}发出请求:`, this.value, event)return "throttle return value"
}, 1000, { trailing: true });
throttle("aaaaa").then((res) => {console.log("res", res)
})
自定义深拷贝函数
🔻 前面我们已经学习了对象相互赋值的一些关系,分别包括:
🔸 引入的赋值:指向同一个对象,相互之间会影响;
🔸 对象的浅拷贝:只是浅层的拷贝,内部引入对象时,依然会相互影响;
🔸 对象的深拷贝:两个对象不再有任何关系,不会相互影响;
🔻 前面我们已经可以通过一种方法来实现深拷贝了:
🔸 JSON.parse 这种深拷贝的方式其实对于函数、Symbol等是无法处理的;
🔸 并且如果存在对象的循环引用,也会报错的;
const info = {name: "why",age: 18,friend: {name: "kobe"},running: function() {},[Symbol()]: "abc",// obj: info
}
info.obj = info
// 1.操作一: 引用赋值
// const obj1 = info// 2.操作二: 浅拷贝
// const obj2 = { ...info }
// // obj2.name = "james"
// // obj2.friend.name = "james"
// // console.log(info.friend.name)// const obj3 = Object.assign({}, info)
// // obj3.name = "curry"
// obj3.friend.name = "curry"
// console.log(info.friend.name)// 3.操作三: 深拷贝
// 3.1.JSON方法
// const obj4 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(info))
// info.friend.name = "curry"
// console.log(obj4.friend.name)
// console.log(obj4)
🔻 自定义深拷贝函数:
🔸 1.自定义深拷贝的基本功能;
🔸 2.对Symbol的key进行处理;
🔸 3.其他数据类型的值进程处理:数组、函数、Symbol、Set、Map;
🔸 4.对循环引用的处理;
// 判断数据类型
function isObject(value) {const valueType = typeof value;return (value !== null) && (valueType === "function" || valueType === "object")
}
// 深拷贝
function deepCopy(originValue, map = new WeakMap()) {// 如果值是Symbol类型if (typeof originValue === "symbol") {return Symbol(originValue.description)}// 如果是原始类型,直接返回if (!isObject(originValue)) {return originValue}// 如果有Set类型if (originValue instanceof Set) {const newSet = new Set();for (const setItem of originValue) {newSet.add(deepCopy(setItem))}return newSet}// 如果是函数function类型, 不需要进行深拷贝if (typeof originValue === "function") {return originValue}// 如果是对象类型,才需要创建对象if (map.get(originValue)) {return map.get(originValue);}// 创建数组const newObj = Array.isArray(originValue) ? [] : {};map.set(originValue, newObj);// 遍历普通的keyfor (const key in originValue) {newObj[key] = deepCopy(originValue[key], map);}// 单独遍历symbolconst keySymbols = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(originValue);for (const symbolKey of keySymbols) {newObj[Symbol(symbolKey.description)] = deepCopy(originValue[symbolKey], map)}return newObj
}
const set = new Set(["abc", "cba", "nba"])
const s1 = Symbol("s1")
const s2 = Symbol("s2")
const info = {name: "why",age: 18,friend: {name: "kobe",address: {name: "洛杉矶",detail: "斯坦普斯中心"}},// 1.特殊类型: Setset,// 2.特性类型: functionrunning: function () {console.log("running~")},// 3.值的特殊类型: SymbolsymbolKey: Symbol("abc"),// 4.key是symbol时[s1]: "aaaa",[s2]: "bbbb",// self: info
}
info.self = info;
const newObj = deepCopy(info);
console.log(newObj);
console.log(newObj === newObj.self);//true
