LeetCode 1605. Find Valid Matrix Given Row and Column Sums【贪心,数组】中等
本文属于「征服LeetCode」系列文章之一,这一系列正式开始于2021/08/12。由于LeetCode上部分题目有锁,本系列将至少持续到刷完所有无锁题之日为止;由于LeetCode还在不断地创建新题,本系列的终止日期可能是永远。在这一系列刷题文章中,我不仅会讲解多种解题思路及其优化,还会用多种编程语言实现题解,涉及到通用解法时更将归纳总结出相应的算法模板。
为了方便在PC上运行调试、分享代码文件,我还建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/memcpy0/LeetCode-Conquest。在这一仓库中,你不仅可以看到LeetCode原题链接、题解代码、题解文章链接、同类题目归纳、通用解法总结等,还可以看到原题出现频率和相关企业等重要信息。如果有其他优选题解,还可以一同分享给他人。
由于本系列文章的内容随时可能发生更新变动,欢迎关注和收藏征服LeetCode系列文章目录一文以作备忘。
You are given two arrays rowSum and colSum of non-negative integers where rowSum[i] is the sum of the elements in the ith row and colSum[j] is the sum of the elements of the jth column of a 2D matrix. In other words, you do not know the elements of the matrix, but you do know the sums of each row and column.
Find any matrix of non-negative integers of size rowSum.length x colSum.length that satisfies the rowSum and colSum requirements.
Return a 2D array representing any matrix that fulfills the requirements. It’s guaranteed that at least one matrix that fulfills the requirements exists.
Example 1:
Input: rowSum = [3,8], colSum = [4,7]
Output: [[3,0],[1,7]]
Explanation:
0th row: 3 + 0 = 3 == rowSum[0]
1st row: 1 + 7 = 8 == rowSum[1]
0th column: 3 + 1 = 4 == colSum[0]
1st column: 0 + 7 = 7 == colSum[1]
The row and column sums match, and all matrix elements are non-negative.
Another possible matrix is: [[1,2],[3,5]]
Example 2:
Input: rowSum = [5,7,10], colSum = [8,6,8]
Output: [[0,5,0],[6,1,0],[2,0,8]]
Constraints:
1 <= rowSum.length, colSum.length <= 5000 <= rowSum[i], colSum[i] <= 108sum(rowSum) == sum(colSum)
题意:给出两个非负整数数组 rowSum 和 colSum ,其中 rowSum[i] 是二维矩阵中第 i 行元素的和, colSum[j] 是第 j 列元素的和。返回大小为 rowSum.length x colSum.length 的任意 非负整数 矩阵,且该矩阵满足 rowSum 和 colSum 的要求。题目保证存在 至少一个 可行矩阵。
解法 贪心
一开始可能很懵逼,但仔细想想就能发现答案。设答案矩阵为 ans ,则要给出 ans[i][j] 时,显然 ans[i][j] <= rowsum[i] && ans[i][j] <= colsum[j] ,即 ans[i][j] 最大为 min(rowsum[i], colsum[j]) 。我们的贪心策略是,按照从左到右、从上到下的顺序,给 ans[i][j] 填上当前可填的最大值。借用大佬做的图:
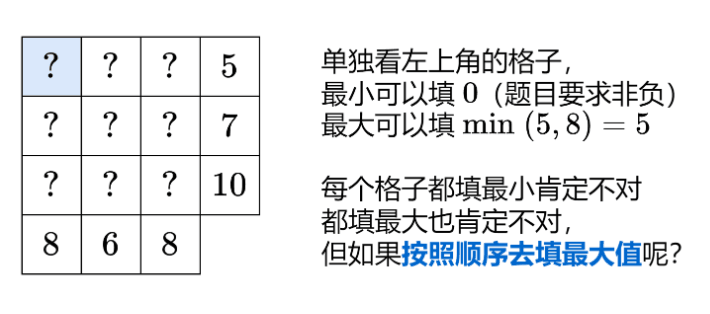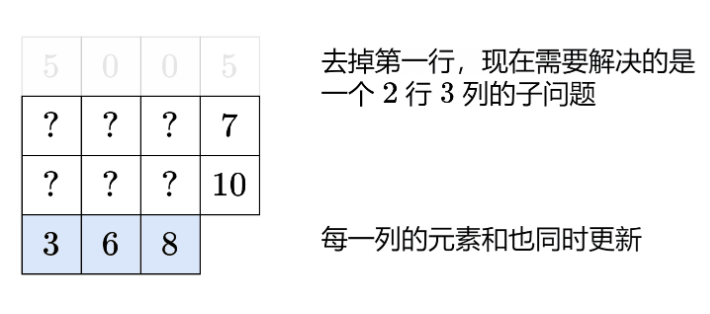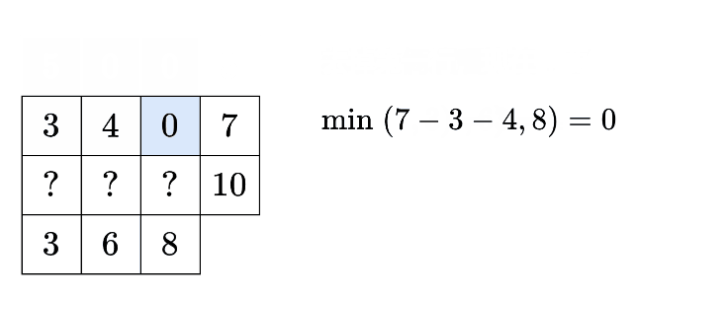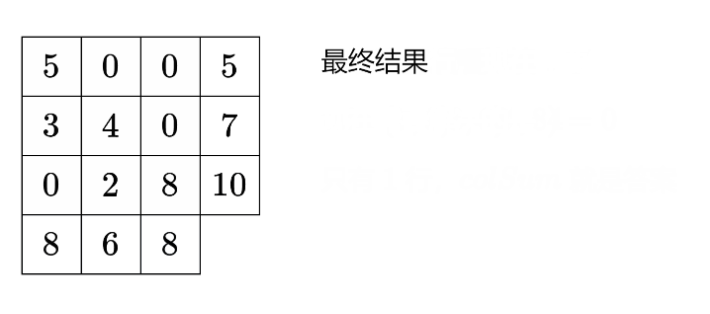
问题是:如何证明该构造方案一定能得到满足题目要求的矩阵?即使感觉上是可行的。
回答是:设生成的矩阵为 ans 。
- 对于只有 111 行的情况,可知各列元素一定小于等于该行元素和即
colSum[j] <= rowSum[0],我们令ans[0][j] = min(rowSum[0], colSum[j]) = colSum[j]。由于题目保证sum(rowSum) == sum(colSum),所以只有 111 行的ans可以满足题目要求。 - 假设前 m−1m−1m−1 行的
ans是满足题目要求的,剩下的是行和、列和数组分别是rowSum, colSum。上述构造方案可满足ans各列分别等于colSum[j]、ans第 mmm 行的和等于rowSum[m-1]。
只要 m−1m-1m−1 行的ans是满足题目要求的,那么第 mmm 行的ans也满足题目要求。 根据数学归纳法, mmm 行的ans是满足题目要求的。
class Solution {
public:vector> restoreMatrix(vector& rowSum, vector& colSum) {int n = rowSum.size(), m = colSum.size();vector> ans(n, vector(m));for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {ans[i][j] = min(rowSum[i], colSum[j]);rowSum[i] -= ans[i][j];colSum[j] -= ans[i][j];}}return ans;}
};
- 时间复杂度:O(mn)O(mn)O(mn)
- 空间复杂度:O(mn)O(mn)O(mn)
还可继续优化。不难发现,我们取 min(rowSum[i], colSum[j]) 时,如果取到的是 rowSum[i] ,则该行的元素已经取完,这一行后面的元素只能取零;如果取到的是 colSum[j] ,则该列的元素已经取完,这一列后面的元素只能取零。这样理解也行:从左上角出发,每次要么去掉一行,要么去掉一列。同样根据数学归纳法,可以证明该做法的正确性。见图:

class Solution {
public:vector> restoreMatrix(vector& rowSum, vector& colSum) {int n = rowSum.size(), m = colSum.size();vector> ans(n, vector(m));for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n && j < m;) {int rs = rowSum[i], cs = colSum[j];if (rs < cs) { // 取rowsum[i],去掉第i行,往下走colSum[j] -= rs;ans[i++][j] = rs;} else { // 去掉第j列,往右走rowSum[i] -= cs;ans[i][j++] = cs;}}return ans;}
};
下一篇:学生社团管理系统的设计与实现
