Machine Learning-Ex1(吴恩达课后习题) Use: MATLAB/Python
来源:吴恩达教授 教学视频课后题目
1. Simple MATLAB function
问题:输出一个5×5的单位矩阵
MATLAB
warmUpExercise.m
function A = warmUpExercise()
A = eye(5);lx.m
fprintf('Running warmUpExercise ... \n');
fprintf('5x5 Identity Matrix: \n');
warmUpExercise()Running warmUpExercise ...
5x5 Identity Matrix:
ans =
1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1
Python
inputIdentityMatrix.py
import numpy as np # NumPy库支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算def inputIdentityMatrix():print(np.eye(5))lx.py
from inputIdentityMatrix import *inputIdentityMatrix()[[1. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]]
2. Linear regression with one variable
数据:
第一列:给出城市人口数量
第二列:该城市饭店的收益
2.1 Plotting the Data
MATLAB
plotData.m
function plotData(x,y)
% r:red--x:用x作标记--MarkerSize:标记符的大小
plot(x,y,'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10);
xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s');
ylabel('Profit in $10,000s');
title('Scatter plot of training data');
endlx.m
fprintf('Plotting Data...\n')
data = load('ex1data1.txt');
X = data(:,1); % data第一列赋值给X向量
y = data(:,2); % data第二列赋值给y向量
m = length(X); % No. of training setplotData(X,y);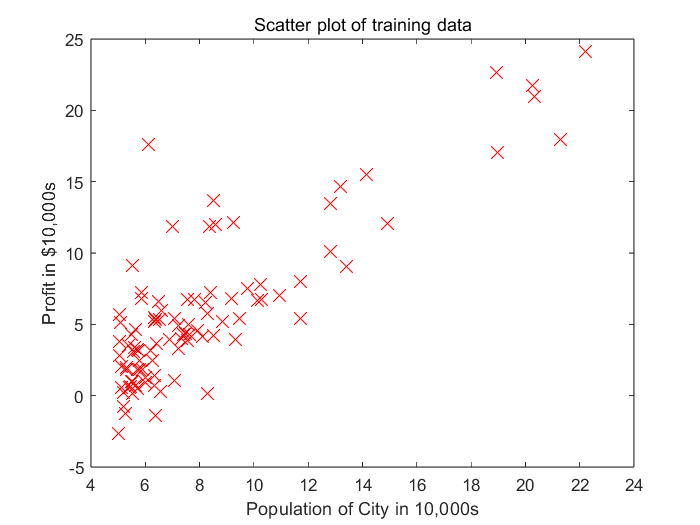
Python
lx.py
import pandas as pd # 一种用于数据分析的扩展程序库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # matplotlib是一种数据可视化库# header=None:无列标题行 names命名,data为DataFrame类型
# read_csv 以纯文本形式存储表格数据(数字和文本)
data = pd.read_csv('ex1data1.txt', header=None, names=['Population', 'Profit'])# DataFrame类型与plot函数结合使用
data.plot(x='Population', y='Profit', kind='scatter', marker='x')
plt.show() # 展示图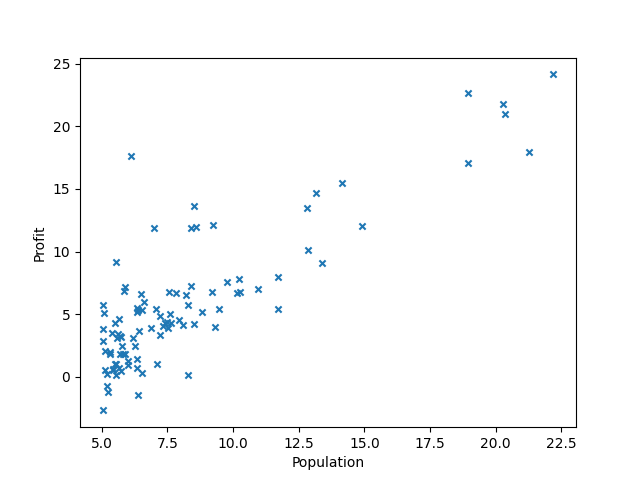
2.2 Gradient Descent
2.2.1 Update Equations
Cost Funtion:

Update Equations:
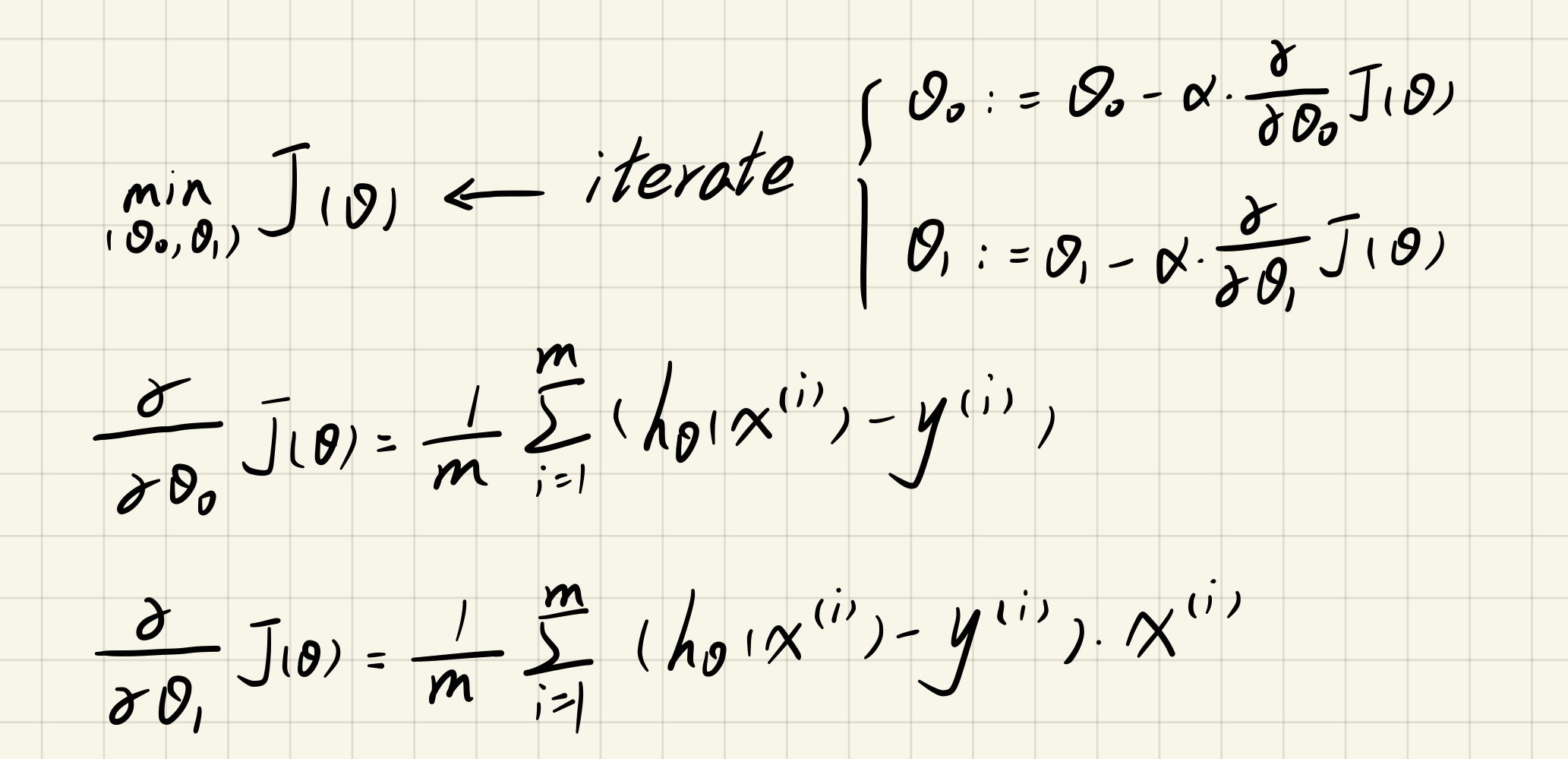
2.2.2 Computing the cost J(theta)
绘制J(theta)图像
MATLAB
computeCost.m
function J = computeCost(X,y,theta)
predictions = X * theta; % 预测值
sqrErrors = (predictions - y).^2; % 误差的平方
J = 1 / (2 * length(X(:,1))) * sum(sqrErrors);
endlx.m
data = load('ex1data1.txt');
m = length(data(:,1)); % No. of training set
X = [ones(m,1),data(:,1)]; % 设置X向量
y = data(:,2); % 设置y向量
theta = zeros(2,1); % theta设置为两行一列的0向量
alpha = 0.01; % learning rate fprintf('\nTesting the cost function ...\n');
J = computeCost(X,y,theta);
fprintf('With theta = [0 ; 0]\nCost computed = %f\n', J);J = computeCost(X, y, [-1 ; 2]);
fprintf('\nWith theta = [-1 ; 2]\nCost computed = %f\n', J);Testing the cost function ...
With theta = [0 ; 0]
Cost computed = 32.072734
With theta = [-1 ; 2]
Cost computed = 54.242455
Python
import pandas as pd # 一种用于数据分析的扩展程序库
import numpy as np # NumPy库支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # matplotlib是一种数据可视化库def computeCost(theta, X, y):inner = np.power((X * theta.T - y), 2)# sum与np.sum的区别:sum不能处理二维及二维以上的数组return np.sum(inner) / (2 * len(X))data = pd.read_csv('ex1data1.txt', header=None, names=['Population', 'Profit'])
data.insert(0, 'Ones', 1) # 第0列插入名为Ones的值为1的一列
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data.iloc[:, :-1] # iloc的用法[a:b,c:d]表示行从a到b-1,列从c到d-1
# data.shape[0]是行数
# data.shape[1]是列数
y = data.iloc[:, cols - 1:cols]# 将X和y变成矩阵的形式
X = np.matrix(X)
y = np.matrix(y)
theta = np.matrix([0, 0])# 观察维度
# print(X.shape, theta.shape, y.shape) # (97, 2) (2, 1) (97, 1)print(computeCost(theta, X, y)) # 32.0727338774556762.2.3 Gradient descent
目的:通过改变theta的值,来最小化代价函数J(theta)。

MATLAB
gradientDescent.m
function [theta,J_history] = gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,num_iters)
m = length(y); % number of training examples
J_history = zeros(num_iters,1); % 设置代价函数J(theta)初始化为0% 进入迭代
for iter = 1:num_iterstheta_temp = theta; % 保证同时调整theta值for i = 1:length(theta) % 这里指theta0和theta1% 矩阵的转置可以用.'来表示,(:,i)即使用第i列theta_temp(i) = theta(i)-alpha/m*(X*theta-y).'*X(:,i);endtheta = theta_temp;% 保存每一次迭代后代价函数的值J_history(iter) = computeCost(X,y,theta);
end
endlx.m
data = load('ex1data1.txt');
m = length(data(:,1)); % No. of training set
X = [ones(m,1),data(:,1)]; % 设置X向量
y = data(:,2); % 设置y向量
theta = zeros(2,1); % theta设置为两行一列的0向量
alpha = 0.01; % learning rate % 分布
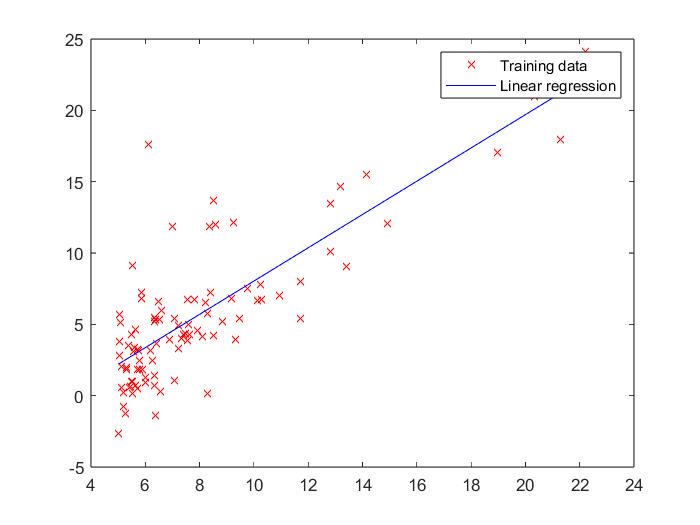
plot(X(:,2),y,'rx');num_iters = 1500;
theta = gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,num_iters);
fprintf('Theta found by gradient descent:\n');
fprintf('%f\n',theta);fprintf('Expected theta values (approx)\n');
fprintf(' -3.6303\n 1.1664\n\n');hold on; % 后者可覆盖在前者图上
plot(X(:,2),X*theta,'b-');
legend('Training data', 'Linear regression')
hold off; % 关闭后,后者不可覆盖在前者图上% Predict values for population sizes of 35,000 and 70,000
predict1 = [1,35000]*theta;
fprintf('For population = 35,000, we predict a profit of %f\n',predict1);
predict2 = [1,70000]*theta;
fprintf('For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of %f\n',predict2);Theta found by gradient descent:
-3.630291
1.166362
Expected theta values (approx)
-3.6303
1.1664
For population = 35,000, we predict a profit of 40819.051970
For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of 81641.734232
Python
Function.py
import numpy as np # NumPy库支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算# 代价函数
def computeCost(theta, X, y):inner = np.power((X * theta.T - y), 2)# sum与np.sum的区别:sum不能处理二维及二维以上的数组return np.sum(inner) / (2 * len(X))# 梯度下降
def gradientDescent(X, y, theta, iter_nums, alpha):X = np.matrix(X)y = np.matrix(y)# ravel用于将矩阵拉伸,shape[1]-返回列数temp_theta = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape)) # temp_theta用于theta1和theta2同步进行更新para_nums = int(theta.ravel().shape[1]) # para_num为2,分别是theta0和theta1J_history = np.zeros(iter_nums) # 用来记录每一次迭代后代价函数的值for i in range(iter_nums):inner = X * theta.T - yfor j in range(para_nums):temp_theta[0, j] = theta[0, j] - (alpha / len(X)) * inner.T * X[:, j]theta = temp_thetaJ_history[i] = computeCost(theta, X, y)return theta, J_historylx.py
import pandas as pd # 一种用于数据分析的扩展程序库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # matplotlib是一种数据可视化库
import numpy as np # NumPy库支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算
from Function import *data = pd.read_csv('ex1data1.txt', header=None, names=['Population', 'Profit'])
data.insert(0, 'Ones', 1) # 第0列插入名为Ones的值为1的一列
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data.iloc[:, :-1] # iloc的用法[a:b,c:d]表示行从a到b-1,列从c到d-1
y = data.iloc[:, cols - 1:cols]
theta = np.matrix([0, 0])
alpha = 0.01
iter_nums = 1500final_theta, Cost_J = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, iter_nums, alpha)print('Theta found by gradient descent:')
print(final_theta)# linspace(a,b,c)-将a-b区间分为c份
x = np.linspace(data.Population.min(), data.Population.max(), 100)
h_theta_ = final_theta[0, 0] + final_theta[0, 1] * x
# fig代表绘图窗口(Figure),ax代表此绘图窗口的坐标系(axis),subplots用于创建子图
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
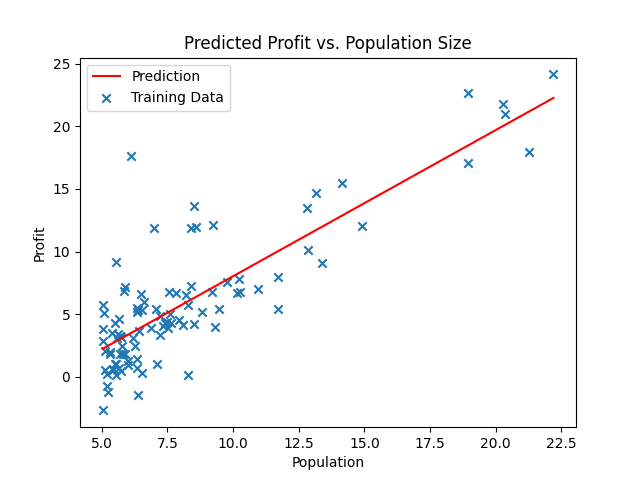
ax.plot(x, h_theta_, 'r', label='Prediction')# Predict values for population sizes of 35,000 and 70,000
predict1 = [1, 35000] * final_theta.T
print('For population = 35,000, we predict a profit of %f' % predict1);
predict2 = [1, 70000] * final_theta.T
print('For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of %f' % predict2);# 画出离散的点
ax.scatter(data.Population, data.Profit, marker='x', label='Training Data')
ax.legend(loc=2) # loc位置,放在左上角
ax.set_xlabel('Population')
ax.set_ylabel('Profit')
ax.set_title('Predicted Profit vs. Population Size')
plt.show()Theta found by gradient descent:
[[-3.63029144 1.16636235]]
For population = 35,000, we predict a profit of 40819.051970
For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of 81641.734232
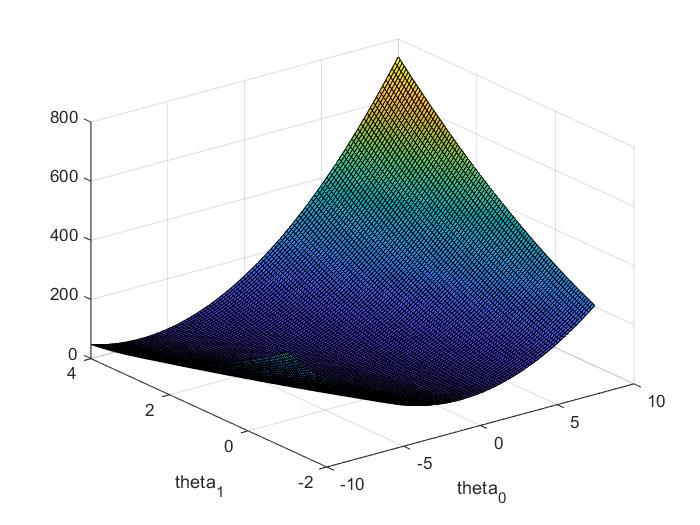
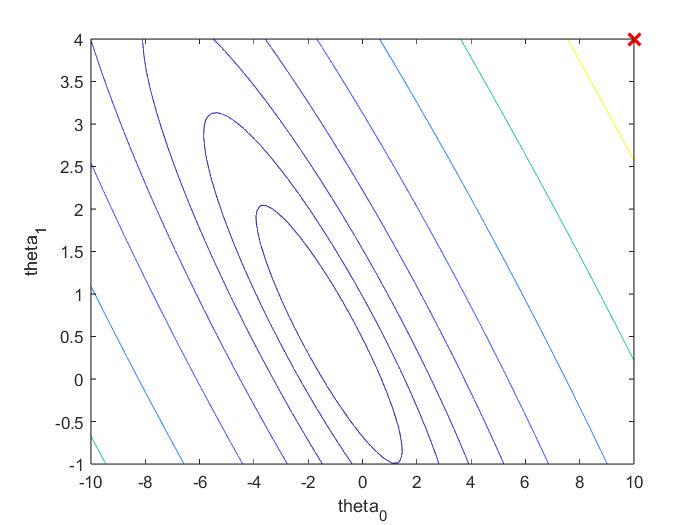
2.3 Visualizing J(theta)
关于:theta0、theta1不断变化时,J(theta)的变化
lx.m
data = load('ex1data1.txt');
m = length(data(:,1));
X = [ones(m,1),data(:,1)]; % 设置X向量
y = data(:,2); % 设置y向量fprintf('Visualizing J(theta0, theta1) ...\n')theta0_vals = linspace(-10,10,100);
theta1_vals = linspace(-1,4,100);
J_vals = zeros(length(theta0_vals),length(theta1_vals));for i = 1:length(theta0_vals)for j = 1:length(theta1_vals)theta = [theta0_vals(i);theta1_vals(j)]; % 中间用分号表示列向量J_vals(i,j) = computeCost(X,y,theta);end
endfigure;
surf(theta0_vals,theta1_vals,J_vals);
xlabel('theta_0');
ylabel('theta_1');
figure;
contour(theta0_vals,theta1_vals,J_vals,logspace(-2, 3, 20));
xlabel('theta_0'); ylabel('theta_1');
hold on;
% theta此时为[10,4]
plot(theta(1), theta(2), 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 2);
hold off;